How to help keep your baby safe
Entering the world of parenthood comes with its fair share of anxiety, from wondering how different your new life will be, to the worry of being responsible for a new little person. Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), previously known as ‘cot death’, is the unexplained death (typically during sleep) of a seemingly healthy baby. While SIDS is a very real threat, with a little knowledge you can reduce many known contributing factors.
Back to sleep
You’ll no doubt hear this on repeat from midwives and Plunket nurses as soon as your little babe comes along and for very good reason. Babies who sleep on their stomachs are much more at risk of SIDS. While it’s not 100% understood exactly why experts believe it could be about re-inhaling stale air. Once your baby can happily roll over by themself, you don’t need to worry about sleeping positions any more.
Make it a strictly smoke-free zone
Smoking (and exposure to second-hand smoke) during pregnancy not only puts your baby at risk of health issues but increases the risk of SIDS too. It’s thought that nicotine can wreak havoc on a mechanism in their brain which senses a lack of oxygen and triggers breathing to start (called auto-resuscitation). So make sure it’s strictly a smoke-free zone when you’re pregnant and when your little one arrives, and that your family and friends are on board too.
Welcome your new (temporary) roommate
It’s widely recommended that your new babe bunks in with you (in their own safe sleeping space) for at least the first four to six months. This isn’t always practical for light sleepers, in which case a good breathing movement monitor set up in their nursery will give you peace of mind.
A safe spot for slumber
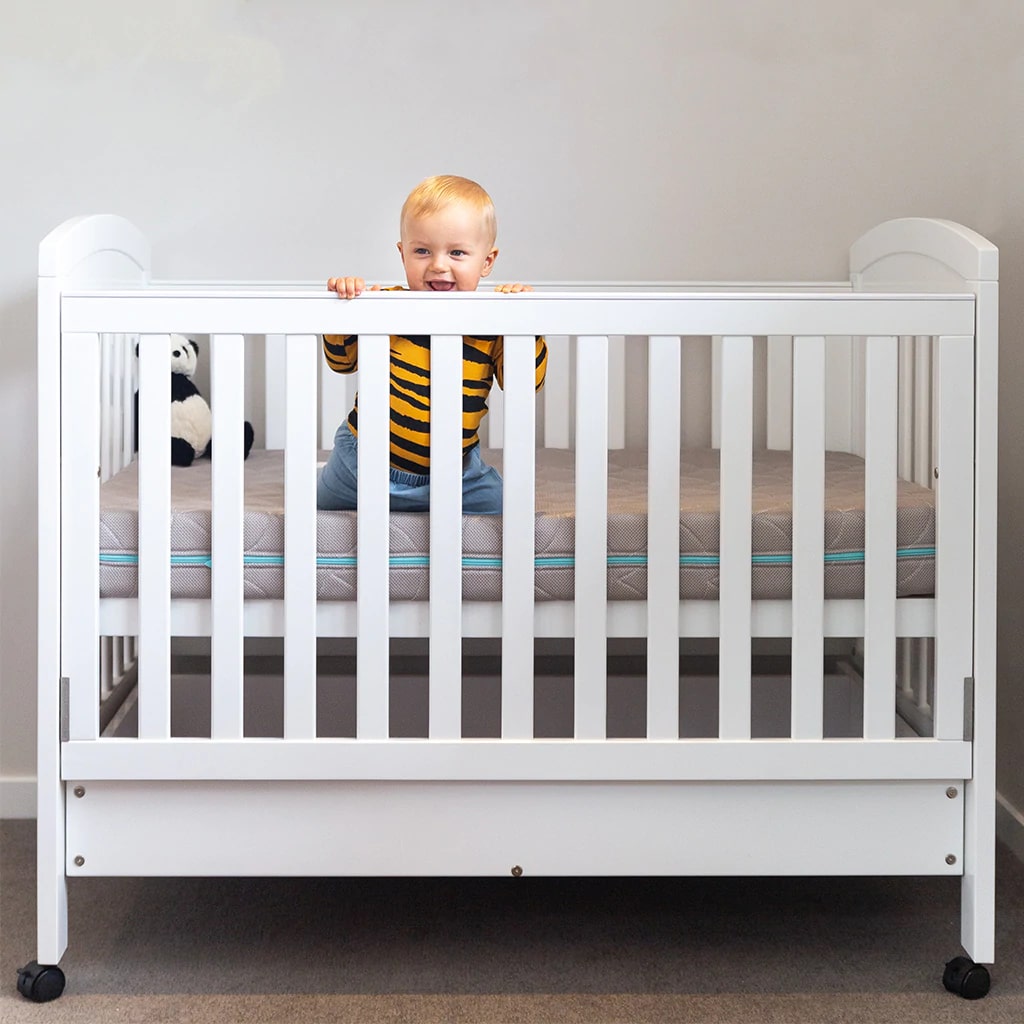
While room-sharing is recommended, bed-sharing isn’t. It can be so tempting to savour that extra time snuggled up in bed with your new babe, but bulky duvets, pillows and even an adult rolling can spell danger for little ones. Setting your baby up with their own safe space (like a portable Moses basket ) within arm’s reach is your best option.
Be prepared to be suddenly jolted awake and find yourself sitting up in bed or a nursing chair with your baby in your arms – sleep deprivation can really grab hold of you in the early days. Sleeping with a baby on a chair or sofa is very dangerous, so to avoid this as much as possible, use the middle-of-the-night feeds as opportunities to clear out and edit that day’s photos on your phone (no doubt there will be plenty!) Your phone’s blue light will help keep you alert.
Baby, it’s cold outside
It’s important to make sure the room where your baby is sleeping is at a comfortable temperature. Bundling up babies at all times is an outdated theory – overheating is another substantial SIDS risk. Higher temperatures can put babies into a deeper slumber, making it difficult for them to wake if their breathing is obstructed. The recommended room temperature for a baby is 16 to 20 degrees, with around 18 degrees being ideal. To check your baby’s temperature, feel his back or tummy – it should feel warm. A great way to check the temperature of their nursery is with a combined nightlight/temperature sensor like the Moon Nightlight .
Blankets (and everything else) be gone
All those cute blankets, animal-shaped pillows and snuggly little toys that create a cosy-looking cot will need to stay in storage until your baby’s first birthday. Until then, all you need is a fitted sheet and wearable bedding like a Merino Sleep Pod to keep them warm. The key is to avoid anything that may cover their face and restrict breathing.
Breastfeed if possible
Experts aren’t sure why, but breastfeeding can significantly lower the risk of SIDS. The theory is that breastfeeding promotes the sucking and swallowing action, which develops muscles that keep the airway open while boosting brain development. Breastfed babies are generally lighter sleepers, too. This might not sound like a benefit at 2 am, but anything that helps reduce SIDS is a big plus.
A big tick for pacifiers
There tends to be negativity around using pacifiers, but they can not only be life-saving for unsettled babies during car trips, but also literally life-saving. Once again, it’s a bit of an unknown how pacifiers help, but there is a clear link – babies who use pacifiers are at lower risk of SIDS. As with breastfeeding, this could be due to more developed sucking and swallowing muscles that help keep airways open. If you’re breastfeeding, wait until this is well established (at least 4-6 weeks) before introducing a good quality silicone pacifier .
Do what you can to reduce the risk
While there are still a lot of unknowns with SIDS, being armed with what you can do to reduce as many risks as possible should put your mind at ease. Keep in mind that the risk of SIDS decreases after six months and is pretty rare after a baby’s first birthday.